No Jargon: What is Artificial Intelligence in Simple Words

Searching for the simplest meaning of artificial intelligence? Look no further.
I have defined artificial intelligence in simple words, accompanied by real-life examples.
To understand what artificial intelligence is, we need to first understand two definitions: intelligence and machine.
Intelligence
Intelligence, in a broad sense, is the ability to think, solve problems, make decisions or strategies or adapt to new situations.
Intelligence involves learning previous knowledge and experiences and applying knowledge in practical situations to help dealing with current or future situations or challenges.
It’s like utilizing what you know, what we have learned, and sometimes even adjusting that knowledge to handle new, unfamiliar scenarios effectively.
The knack for adapting, learning from past experiences, and applying knowledge in practical situations is a fundamental aspect of intelligence.
The Evolution of Intelligence
Using our intelligence, our ancestors started to use fire, cook food, and cultivate crops to make our lives easier. They utilized their emerging intelligence in numerous resourceful and adaptive ways.
One likely example could be the way they dealt with predators and hunting. Perhaps after some unfortunate incidents, through observation and learning, they understood that hunting larger prey or dealing with dangerous animals poses significant risks.
Therefore, they may started to use certain tools or tactics like group hunting or creating simple weapons which could maximize their chances of a successful hunt and minimize their risk.
So, they exhibited intelligence because by learning from the past experience and using that information to develop primitive weapons and make strategies for hunting methods, which not only enhanced their food sources but also increased their safety.
Concerning fire, our ancestors might have noticed that fire could be both a source of warmth and a method for keeping predators at bay. Utilizing this knowledge, they learned to control fire for their benefit, also discovering that cooked food could be more nutritious and safer to consume.
This demonstrates again an important utilization of intelligence – observing, learning, and then innovatively applying knowledge to improve their survival and quality of life.
Like human, all animals exhibit a basic form of intelligence to survive.
These early uses of intelligence have paved the way for our advanced problem-solving abilities and made us different from the rest of animals.
Machine
Just as our ancestors used their intelligence to innovate and adapt, we have channeled our intelligence into creating machines.
Machine is a tool that performs the intended task to ease our productivity or tool that needs human assistance to operate.
For instance, a car is a machine that needs driver to operate and without the driver, it cannot go by itself. In case of machine, it cannot think on its own to operate; it needs human intervention. In the case of digital machines, they repeat or execute a set of instructions set by human beings.
For instance, the traditional traffic or traffic lights at your local area operate according to rules or programs that are set by engineers on the microcontroller chips. The instructions are it must change the light from red to green or from yellow to red.
Whether it is a simple plough tool, a bigger machine, or a computer, they perform their intended tasks with the help of human beings.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
What if machine can think and operate by itself and does not need humans? What if machine starts to mimic intelligence? Then, we will call the machine artificial intelligence.
So, artificial intelligence in simple words is an advanced machine that has intelligence or a non-biological machine that can mimic intelligence.
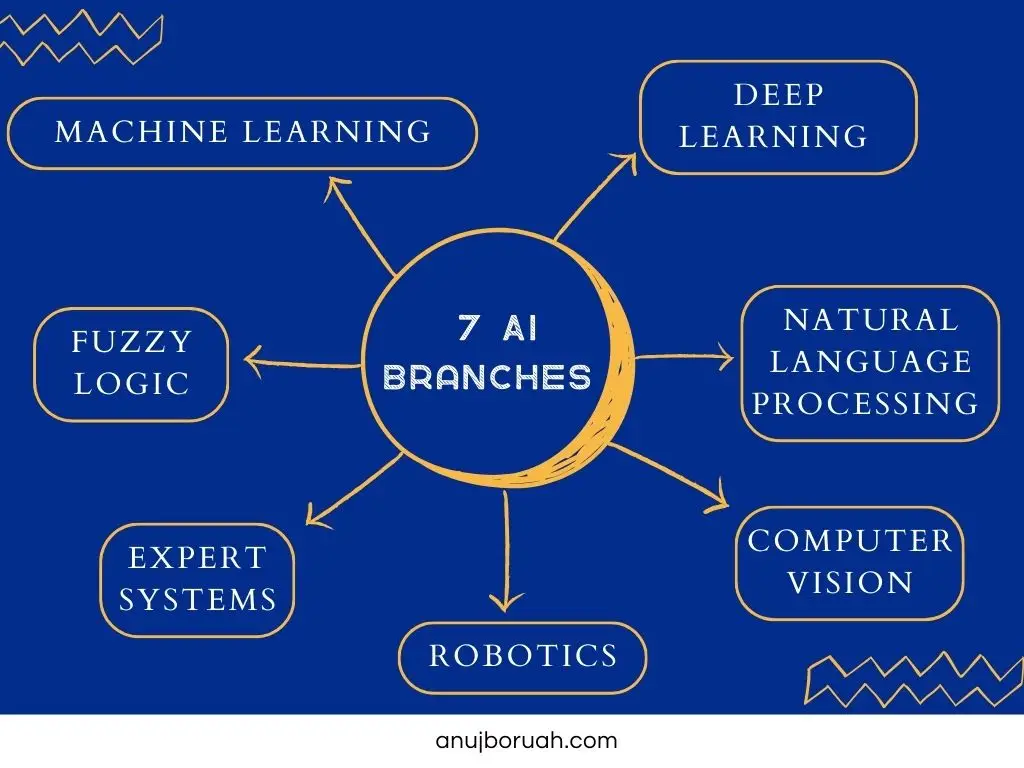
Artificial intelligence is an umbrella term that encompasses various fields such as Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Natural Language Processing, Computer Vision, Robotics, Robotics, Expert Systems, and Fuzzy Logic. It is an amalgamation of many fields.
AI can imitate many aspects of human intelligence, but there are some differences between the two.
Why do we consider advanced machine intelligent?
Artificial Intelligence, or AI shares similarities with human intelligence in the way it uses previous knowledge to make decisions or solve problems. AI systems learn from data and experiences, and then they apply that learned knowledge to perform tasks, make decisions, or even predict future outcomes.
Examples of AI
Example 1: Traffic Lights
Let’s take the earlier examples. you are about to cross your local traffic light at midnight or around 2 a.m when there are no humans around you. Despite the absence of humans, the traffic light, which is a machine, shows you the red light.
You may feel irritated, but the machine is doing or executing what it is supposed to do.
But if the traffic light has thinking capabilities and can perceive its environment and make decisions or become adaptive to the environment, then instead of showing you the red light at 2 a.m. or when there are no humans, it will show you the green light instantly.
Many countries, such as the United States, China, South Korea, Japan, Israel, Singapore, Germany, Australia, India, etc., are using AI-powered traffic lights. In India, states like Goa, union territory Delhi, and cities like Bengaluru are using AI-powered traffic lights.
In the case of normal traffic lights, they use timer systems, but AI-powered traffic lights are adaptive. They can monitor traffic and adjust the timing of traffic lights based on real-time traffic conditions. This can help reduce congestion and improve traffic flow.
Here is How It Works
AI-powered traffic lights work by leveraging a combination of technologies like sensors, cameras, and data analytics, along with machine learning algorithms, to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion.
Cameras and sensors are deployed at intersections to monitor real-time traffic conditions. They capture various data points like vehicle count, speed, and wait times at each light. This data is then fed into a system equipped with machine learning algorithms.
These algorithms analyze the data and predict traffic conditions, learning over time to anticipate typical traffic patterns at different times and days. By continuously analyzing this data, the AI system can adapt the timing of the lights to optimize traffic flow.
For instance, it might extend the green light duration on a particularly busy road to alleviate congestion.
Furthermore, AI traffic lights can communicate with each other through an interconnected system, enabling coordinated adjustments across multiple intersections.
For instance, if one light adjusts to accommodate a burst of traffic, nearby lights can adjust accordingly to maintain smooth flow and prevent bottlenecks.
These intelligent systems, by dynamically adapting to real-time conditions and learning from recurring patterns, offer a stark contrast to traditional traffic lights which operate on fixed timers or simple sensor-trigger mechanisms.
AI-powered traffic lights can detect vehicles and pedestrians more accurately than traditional traffic lights. This can help improve safety at intersections.

Example 2: Self-Driving Car
If a car, which generally needs human beings to control it, can automatically drive like a human being, it is an example of Artificial Intelligence.
An autonomous car uses the knowledge and data it has accumulated from various sensors and previous drives to navigate the road, avoid obstacles, and reach its destination safely.
It learns from the data about what actions (like steering, braking, or accelerating) led to safe driving and tries to repeat them in similar situations in the future.
Tesla cars are famous for their self-driving feature. Imagine a car that can drive by itself. If a self-driving car runs in a remote area of India, what would people say? Recently, Minus Zero, a Bengaluru startup, launched zPod, a self-driving e-rickshaw, and it has become India’s first autonomous vehicle.
Here is How An Autonomous Car Works
Technically speaking, autonomous vehicles integrate a range of sensors, lidars (which use lasers to send out pulses and measure how long it takes for them to return, thus detecting objects), and cameras to perceive their environment. They generate a 3D map of their surroundings by collecting data on road conditions, obstacles, pedestrians, and other vehicles.
Further, for navigation, autonomous cars utilize high-definition maps and GPS data to determine optimal routes to their destinations. They also leverage V2X (Vehicle to Everything) communication, enabling them to interact with other vehicles, traffic management systems, and even pedestrians to enhance situational awareness and improve decision-making.
Once the vehicle perceives its surroundings, machine learning algorithms, and artificial neural networks interpret this sensory input to make driving decisions. They process the data, recognizing patterns and making predictions, like anticipating the actions of other road users.
The vehicle’s control system uses the interpreted data to send operational instructions to the car’s actuators, which control acceleration, braking, and steering. These instructions are generated based on predictive models and real-time adjustments to navigate safely to the destination.
Machine vs. Intelligent Machine
Some distinctions between machine and advanced machines or AI are:
| Machine | AI |
|---|---|
| In case of machine, it needs human intervention. | AI does not need human after the initial phase. |
| Machine cannot upgrade by itself or learn by itself. | An advanced machine can learn by itself. |
Summary of the Blog Post
Intelligence is the ability to think, solve problems, adapt to new situations, and make decisions based on prior knowledge and experiences. Example: Our ancestors used intelligence to control fire, cook food, and develop hunting tactics.
Machine is a tool designed to perform specific tasks, requiring human intervention. For instance, the Traditional traffic lights operate based on pre-set instructions by engineers.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a machine that can mimic human-like intelligence and operate autonomously. AI systems learn from data and make decisions similar to human intelligence.
Examples of AI include AI-Powered Traffic Lights, Self-Driving Cars.
The differences between machine vs. intelligent Machine are the traditional machines need human intervention and can’t learn or upgrade by themselves.
AI systems can learn autonomously and adapt over time.
References
Agrawal, Ajay, Joshua Gans, and Avi Goldfarb. “What to expect from artificial intelligence.” (2017): 1486511104226.
